In today’s interconnected world, cloud security is paramount. Businesses and individuals alike rely heavily on cloud services for data storage, application hosting, and more. However, this reliance also presents significant security risks. Data breaches, malware attacks, and unauthorized access can have devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Therefore, understanding how to secure your cloud data effectively is no longer optional, but a necessity. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to implementing robust security measures to protect your valuable information in the cloud.
This guide will cover essential strategies for cloud data security, encompassing various aspects from access control and encryption to incident response and disaster recovery. We will explore best practices for choosing a secure cloud provider, implementing strong password policies, and leveraging multi-factor authentication. Furthermore, we’ll delve into the importance of data encryption both in transit and at rest, as well as the crucial role of regular security assessments and vulnerability scanning. By following the advice presented here, you can significantly enhance the security posture of your cloud environment and mitigate the risks associated with cloud computing.
Why Cloud Data Security Is Crucial
In today’s interconnected world, data resides at the heart of every business operation. Migrating this valuable asset to the cloud offers numerous benefits, but also introduces significant security risks. Protecting cloud data is crucial for maintaining business continuity, complying with regulations, and preserving trust with customers.
Data breaches can have devastating consequences, resulting in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Robust cloud security measures are essential to mitigate these risks and safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, modification, or deletion.
Furthermore, various industry regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, mandate strict data protection standards. Implementing strong cloud security practices is not just a best practice but a legal imperative for organizations handling sensitive personal or health information.
Common Cloud Security Threats
Understanding common cloud security threats is crucial for effective data protection. Data breaches are a significant concern, often resulting from exploited vulnerabilities or insider threats. Misconfigurations and inadequate access controls leave cloud resources susceptible to unauthorized access. Account hijacking poses a severe risk, enabling attackers to control cloud accounts and potentially sensitive data. Denial of service (DoS) attacks can disrupt service availability, impacting business operations. Malware infections can compromise cloud environments, stealing data or disrupting services. Diligent security measures are essential to mitigating these risks.
Using Strong Encryption Methods
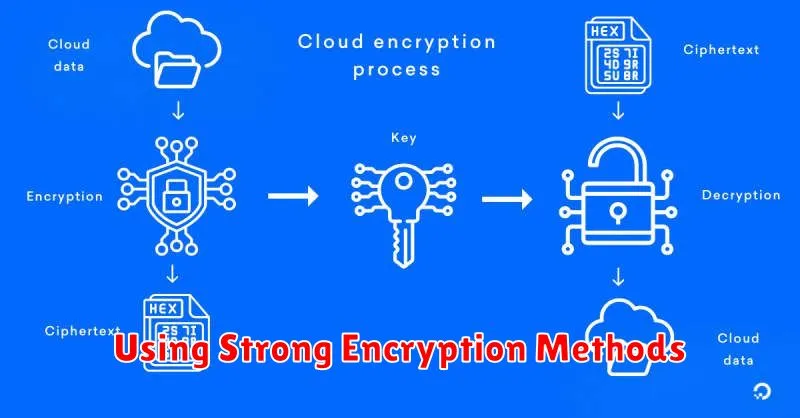
Encryption is crucial for securing your cloud data. It transforms your data into an unreadable format, protecting it even if unauthorized access occurs. Choose robust encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a key size of 256 bits or higher.
Consider implementing encryption at rest, which protects stored data, and encryption in transit, which secures data as it moves between your systems and the cloud. Utilize strong key management practices, including secure key generation, storage, and rotation.
Role of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) plays a critical role in securing cloud data. It adds an extra layer of security beyond just a username and password.
With MFA enabled, even if credentials are compromised, unauthorized access is significantly more difficult. MFA requires users to verify their identity through multiple factors, such as something they know (password), something they have (security token or smartphone), or something they are (biometric verification).
This makes it exponentially harder for attackers to gain access, even if they have obtained a user’s password through phishing or other means. By implementing MFA, organizations significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Data Backup and Recovery Plans
A robust data backup and recovery plan is crucial for cloud security. Regular backups ensure data availability in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or a security breach. Your plan should outline the frequency of backups, the data retention period, and the recovery procedures.
Consider implementing the 3-2-1 backup strategy: 3 copies of your data on 2 different media, with 1 copy stored offsite. This method provides redundancy and protects against various data loss scenarios. Test your recovery procedures regularly to ensure they function as expected and that your recovery time objectives (RTOs) are met.
Access Control Best Practices
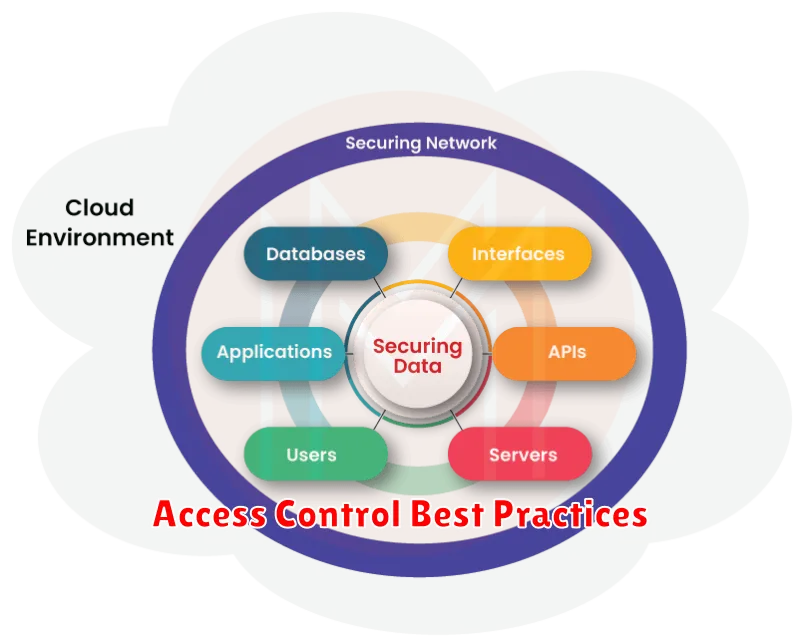
Implementing robust access control is crucial for securing your cloud data. Principle of Least Privilege should be the foundation, granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their duties. Regularly review and revoke unnecessary access to prevent unauthorized data exposure.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even if they compromise credentials. Combine MFA with strong password policies to enforce complex and unique passwords.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) simplifies management by grouping users with similar roles and applying permissions to the group. This streamlines the process and ensures consistent application of access policies.
Security Audits and Monitoring Tools
Regular security audits are crucial for maintaining a strong security posture in the cloud. These audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry regulations. They can be conducted internally or by external security experts.
Leveraging cloud-based security monitoring tools provides real-time visibility into your cloud environment. These tools track user activity, resource usage, and security events, allowing you to quickly detect and respond to potential threats. They offer features like intrusion detection, vulnerability scanning, and security information and event management (SIEM).

