Choosing the right cloud solution for your business is a critical decision. This article explores the key differences between private cloud and public cloud, two prominent cloud computing models. Understanding the distinctions between these options is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with your organization’s specific needs, security requirements, and budget considerations. We will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of each, focusing on aspects like security, control, scalability, and cost, to help you determine whether a private cloud or a public cloud solution, or perhaps a hybrid approach, is the optimal choice for your enterprise.
Navigating the complexities of cloud computing can be challenging. This comparison of private cloud vs. public cloud will provide a clear understanding of each model. We will examine the core characteristics of each, including their infrastructure, management responsibilities, and performance characteristics. By the end of this article, you will be well-equipped to assess the benefits and drawbacks of both private and public cloud environments and confidently select the cloud deployment model that best suits your business objectives and technical requirements. We will also briefly touch upon the concept of hybrid cloud, which combines elements of both private and public clouds, offering a flexible alternative.
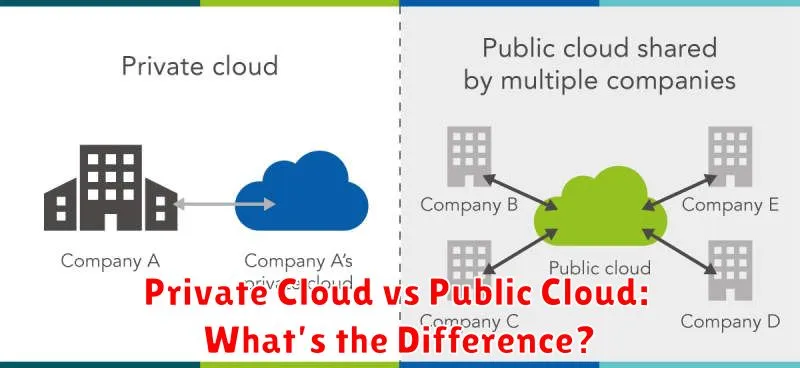
Overview of Public and Private Cloud
Public clouds are cloud computing services offered by third-party providers over the public internet. These providers manage all underlying infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking. Users access resources and services on demand, paying only for what they consume. Public clouds offer scalability and flexibility, making them suitable for a wide range of workloads.
In contrast, private clouds are dedicated cloud environments exclusively used by a single organization. They can be hosted on-premises or managed by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer greater control over security and compliance, making them ideal for sensitive data and applications.
Benefits of Using a Private Cloud
Private clouds offer several key advantages for organizations with specific needs. Enhanced security is a primary benefit, as the infrastructure is solely dedicated to a single organization, reducing the risk of external breaches. This isolation also provides greater control over data, security protocols, and compliance requirements.
Customization is another significant advantage. Private clouds can be tailored to meet precise business needs, offering greater flexibility in resource allocation and configuration. This can lead to improved performance as resources are optimized for specific workloads. Lastly, private clouds offer greater reliability as the organization has direct control over the infrastructure, minimizing dependence on external providers.
Cost Efficiency of Public Cloud
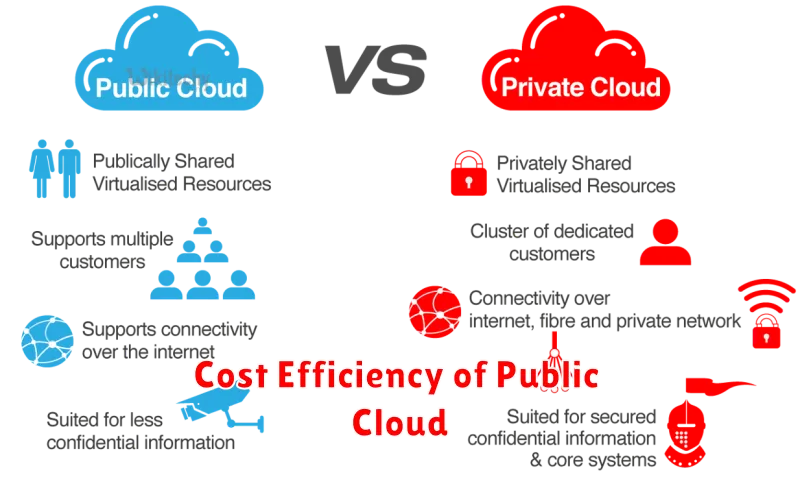
Public cloud offers compelling cost advantages. Pay-as-you-go pricing eliminates upfront investments in hardware and software. This significantly reduces capital expenditure and shifts it to operational expenditure.
Resources are readily scalable, meaning you only pay for what you use. This flexibility avoids over-provisioning and minimizes wasted resources, further optimizing costs. Public cloud providers benefit from economies of scale, translating to lower operating costs for users.
Security and Compliance Comparison
Security and compliance are critical considerations when choosing between private and public cloud deployments. Private clouds offer greater control over security measures, making them suitable for organizations with stringent regulatory requirements or sensitive data. Responsibility for security largely falls on the organization.
Public clouds leverage shared responsibility models. The cloud provider manages the security of the cloud (physical infrastructure, etc.), while the customer is responsible for security in the cloud (data, applications, etc.). Public cloud providers often hold various compliance certifications, potentially simplifying compliance efforts for customers.
Choosing the right deployment depends on the specific security and compliance needs of each organization. A thorough risk assessment is essential.
Performance and Resource Control
A key difference between private and public clouds lies in performance and resource control. With private clouds, organizations have dedicated resources, leading to more predictable performance and greater control over resource allocation. This is especially beneficial for applications with strict performance requirements.
Public clouds, while offering flexibility, share resources among multiple users. This can lead to performance variability depending on the overall load on the cloud provider’s infrastructure. While cloud providers implement resource management strategies, users have less direct control compared to a private cloud environment.
Use Cases for Each Model
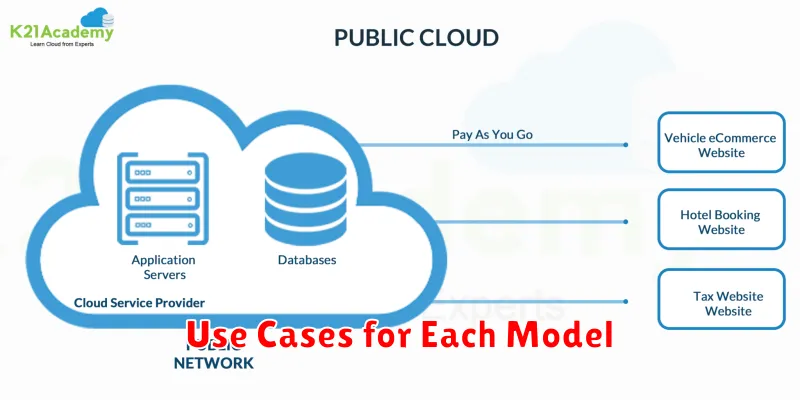
Private Cloud: Organizations with strict regulatory compliance needs, such as those in finance or healthcare, often favor private clouds. This model is also well-suited for businesses requiring high levels of control over their data and infrastructure, and those with unique performance requirements. Lastly, organizations handling sensitive data may prefer a private cloud for enhanced security.
Public Cloud: Public clouds are ideal for startups and small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) due to the lower upfront costs and scalability. Organizations with fluctuating workloads also benefit from the on-demand resource allocation of public clouds. Public clouds are also a suitable choice for disaster recovery and testing and development environments.
Hybrid Cloud as an Alternative
A hybrid cloud model combines the advantages of both private and public clouds. This approach allows organizations to maintain sensitive data on a secure private cloud while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of a public cloud for less critical applications and data.
Hybrid cloud offers greater flexibility, allowing businesses to dynamically adjust resource allocation based on fluctuating demands. This can be particularly beneficial for handling peak loads or seasonal spikes in activity. By strategically distributing workloads, organizations can optimize costs and ensure consistent performance.