In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, website speed and performance are paramount. Slow loading times can lead to high bounce rates, lost conversions, and a negative user experience. This is where a Content Delivery Network (CDN) plays a crucial role, especially in the realm of cloud hosting. A CDN is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to deliver web content, such as HTML pages, javascript files, stylesheets, images, and videos, to users based on their geographic location. By caching content closer to users, CDNs minimize latency, enhance website speed, and improve overall performance.
This article delves into the intricacies of CDNs and their significance in cloud hosting. We will explore how CDNs function, the benefits they offer, and why they are an essential component of any successful online presence. Understanding the power of a CDN is essential for anyone seeking to optimize their website’s performance, improve user experience, and achieve their online goals, particularly in the dynamic world of cloud-based solutions. By leveraging the capabilities of a CDN, businesses can ensure faster loading times, enhanced security, and improved scalability, making it a valuable asset in the competitive online marketplace.
Understanding CDN Basics
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to speed up the delivery of content. These servers store cached copies of your website’s static assets, such as images, videos, and JavaScript files.
When a user requests content from your website, the CDN redirects the request to the server closest to their physical location. This reduces latency, as the content doesn’t have to travel as far, resulting in faster loading times and a better user experience.
Key CDN benefits include improved website performance, reduced server load, and increased availability in case of server outages.
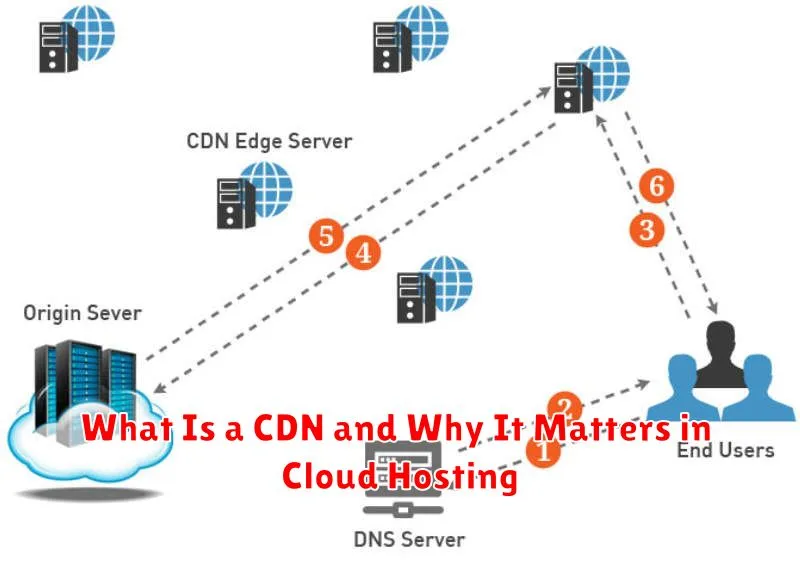
How CDN Works with Cloud Hosting
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) works in conjunction with cloud hosting to optimize content delivery. When a user requests content from a website hosted on a cloud server, the CDN intercepts the request.
The CDN then determines the closest server to the user’s location from its network of distributed servers. If the requested content is already cached on that server, the CDN delivers it directly to the user, reducing latency and improving load times.
If the content is not cached, the CDN retrieves it from the origin server (the cloud hosting server) and caches it for future requests. This process minimizes the load on the origin server and ensures faster delivery for subsequent users in the same geographic region.
Speed and Performance Benefits
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) significantly improves website speed and performance. By caching static content like images, videos, and CSS files on servers geographically closer to users, CDNs reduce latency. This means faster loading times and a smoother user experience, regardless of the user’s location.
Reduced server load is another key benefit. Because the CDN handles a significant portion of the traffic, the origin server experiences less strain. This leads to improved stability and reduces the risk of server crashes, especially during periods of high traffic.
Improved Security and DDoS Protection
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) can significantly bolster your website’s security posture, particularly against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. A CDN’s distributed nature means there isn’t a single point of failure. When attack traffic is directed at your website, the CDN absorbs and distributes it across its network, preventing your origin server from being overwhelmed.
CDNs offer several security features, including Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) and rate limiting. WAFs filter malicious traffic before it reaches your server, mitigating threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting. Rate limiting helps control traffic spikes by throttling requests from suspicious sources, adding another layer of defense against DDoS attempts.
By caching content across multiple servers, CDNs reduce the load on your origin server. This improved resource availability is crucial during DDoS attacks, ensuring legitimate users can still access your website while malicious traffic is being mitigated.
SEO and UX Improvements
Search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience (UX) are intrinsically linked. A fast-loading website is crucial for both. CDNs contribute significantly to improved SEO and UX by reducing latency.
Improved page load speeds lead to lower bounce rates, a key SEO ranking factor. Faster websites provide a more satisfying user experience, encouraging visitors to stay longer and explore more content.
Reduced server load also plays a role. By distributing content closer to users, CDNs lessen the burden on origin servers, ensuring consistent performance even during traffic spikes. This reliability contributes to a positive UX and avoids negative SEO impacts associated with slow or unavailable websites.
Popular CDN Providers
Several companies offer robust and reliable CDN services, catering to various needs and budgets. Selecting the right provider depends on factors like your website’s traffic, geographic reach, and specific requirements. Some popular choices include:
- Cloudflare: Known for its extensive network and security features.
- Amazon CloudFront: Integrated with other Amazon Web Services, providing a comprehensive solution.
- Akamai: A long-standing provider with a large global presence.
- Fastly: Focused on performance and real-time content delivery.
- Google Cloud CDN: Leveraging Google’s infrastructure for reliable and scalable content delivery.
When Should You Use a CDN?
A CDN becomes particularly beneficial in specific scenarios. If your website serves a geographically diverse audience, a CDN is highly recommended. It ensures faster loading times for users located far from your origin server.
If your website experiences high traffic volumes, a CDN can help manage the load by distributing content across multiple servers. This prevents server overload and maintains website availability, even during peak periods.
Websites with static content, such as images, videos, and CSS files, significantly benefit from CDN usage. Caching these assets closer to users reduces latency and improves overall performance. Consider a CDN if security is a top priority. CDNs offer security features like DDoS mitigation to protect your website from attacks.